BSC 链上的攻击:为何发生及其潜在的危害
Authors: | Tofu | CyberPigeon| Beihai |made @BHBA_DAO
BSC 链上的攻击:为何发生及其潜在的危害背景攻击怎么发生的 ?概览攻击详解Solidity 上的默克尔证明IAVL树验证预编译合约核心的漏洞其他潜在攻击针对COSMOS的潜在攻击IBC protocolCosmos-SDK与COSMOS生态桥接的项目Gravity bridgeEVMOS结论我们是谁
背景
币安生态有两条链,其中大家最常用交互的链为BNB chain,这条链由以太坊魔改而成。还有一条链为币安链(Binance Chain),这条链基于 Cosmos SDK 开发而成。由于BNB代币需要在两条链之间流动,因此,BNB chain和 Binance Chain之间有一个币安官方的资产跨链桥,本次受到攻击的就是这个桥。本文会从代码调用角度对这次攻击流程进行详细解析。
攻击怎么发生的 ?
根据 samczsun 的分析, 我们看看币安链的攻击怎么发生的。
概览
首先,我们回顾一下BSC跨链合约的调用流程。
- Relayer向BSC 跨链合约发起一笔交易,调用
handlePackage函数,函数入参数主要为payload和proof。 - 跨链合约根据 默克尔证明 验证
payload的有效性。 - 如果
payload有效, 将payload解析为msgBytes,并发送至 TokenHub Contract 处理消息。 - TokenHub 合约 处理
msgBytes, 接收者从全零地址接收指定数量的BNB代币
在本次攻击中,攻击者发送了一个无效的payload并伪造其证明proof,该证明通过了步骤2中的Merkle证明验证,并成功从TokenHub合约中盗取了200万美元BNB。具体来说,攻击者通过将一个恶意的叶子节点添加到IAVL树的rangeProof中实现proof的伪造,同时该伪造并未引起其默克尔根的计算结果的改变。值得一提,IAVL树是Cosmos团队设计的一种新的数据结构,其结合了Merkle树和AVL树的优点,且IAVL树叶节点的存在性证明与Merkle证明的过程相似。
攻击详解
Solidity 上的默克尔证明
这种攻击是如何发生的? 让我们先来看看跨链合约的调用逻辑。
(1) 在 contracts/CrossChain.sol中, MerkleProof.validateMerkleProof 函数被调用
function handlePackage(bytes calldata payload, bytes calldata proof, uint64 height, uint64 packageSequence, uint8 channelId) onlyInit onlyRelayer sequenceInOrder(packageSequence, channelId) blockSynced(height) channelSupported(channelId) external {
// -- snip --
require( MerkleProof.validateMerkleProof( ILightClient(LIGHT_CLIENT_ADDR).getAppHash(height), STORE_NAME, generateKey(packageSequence, channelId), payloadLocal, proofLocal ), "invalid merkle proof" ); // -- snip --
}
(2)在 contracts/MerkleProof.sol中,函数 function validateMerkleProof 首先将上述步骤(1)中的所有入参组装成十六进制字节码,并通过staticcall调用bnb-chain的0x65预编译合约
function validateMerkleProof(bytes32 appHash, string memory storeName, bytes memory key, bytes memory value, bytes memory proof) internal view returns (bool) { if (appHash == bytes32(0)) { return false; }
// | storeName | key length | key | value length | value | appHash | proof | // | 32 bytes | 32 bytes | | 32 bytes | | 32 bytes | | bytes memory input = new bytes(128+key.length+value.length+proof.length);
// -- snip --
uint256[1] memory result; /* solium-disable-next-line */ assembly { if iszero(staticcall(not(0), 0x65, input, length, result, 0x20)) {} }
return result[0] == 0x01; }}
(3) 在 预编译合约中, func (c *iavlMerkleProofValidate) Run(input []byte) 被调用, 步骤(2)的入参被解析并写入变量kvmp。随后, kvmp.Validate() 被调用
// input:// | payload length | payload |// | 32 bytes | |func (c *iavlMerkleProofValidate) Run(input []byte) (result []byte, err error) { defer func() { if r := recover(); r != nil { err = fmt.Errorf("internal error: %v\n", r) } }()
// -- snip --
kvmp, err := lightclient.DecodeKeyValueMerkleProof(input[precompileContractInputMetaDataLength:]) if err != nil { return nil, err }
valid := kvmp.Validate() if !valid { return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid merkle proof") }
result = make([]byte, merkleProofValidateResultLength) binary.BigEndian.PutUint64(result[merkleProofValidateResultLength-uint64TypeLength:], 0x01) return result, nil}值得一提, kvmp 数据结构定义如下:
kvmp := &KeyValueMerkleProof{ Key: key, Value: value, StoreName: storeName, AppHash: appHash, Proof: &merkleProof,}
IAVL树验证预编译合约
(4) 在 github.com/bnb-chain/bsc/core/vm/lightclient/types.go文件中, 函数 func (kvmp *KeyValueMerkleProof) Validate() 被调用,后续相应调用流程如下
- 首先,跳转到
err := prt.VerifyValue(kvmp.Proof, kvmp.AppHash, kp.String(), kvmp.Value). - 再跳转到
prt.Verify(proof, root, keypath, [][]byte{value}) - 随后跳转到
poz.Verify(root, keypath, args) - 最后跳转到
args, err = op.Run(args)
值得一提,从第1步开始,BSC开始使用 tendermint相关代码库。
具体的调用流程读者可以阅读如下代码
func (kvmp *KeyValueMerkleProof) Validate() bool { prt := DefaultProofRuntime()
//-- snip --
err := prt.VerifyValue(kvmp.Proof, kvmp.AppHash, kp.String(), kvmp.Value) return err == nil}
func (prt *ProofRuntime) VerifyValue(proof *tmcrypto.ProofOps, root []byte, keypath string, value []byte) (err error) { return prt.Verify(proof, root, keypath, [][]byte{value})}
func (prt *ProofRuntime) Verify(proof *tmcrypto.ProofOps, root []byte, keypath string, args [][]byte) (err error) { poz, err := prt.DecodeProof(proof) if err != nil { return fmt.Errorf("decoding proof: %w", err) } return poz.Verify(root, keypath, args)}
func (poz ProofOperators) Verify(root []byte, keypath string, args [][]byte) (err error) { // -- snip --
for i, op := range poz { // -- snip -- args, err = op.Run(args) if err != nil { return } } if !bytes.Equal(root, args[0]) { return cmn.NewError("Calculated root hash is invalid: expected %+v but got %+v", root, args[0]) } // -- snip -- return nil}
(5) 步骤(4)中的opz是由函数 poz, err := prt.DecodeProof(proof)解码proof所得,具体解析结果如下:
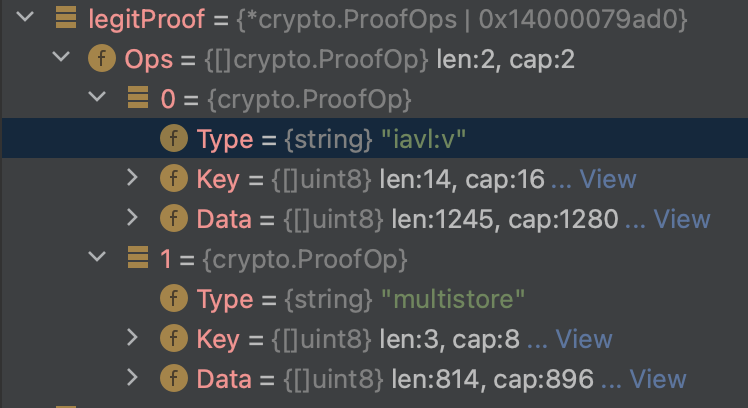
注意。这些 "操作 "指定了计算IAVL树的Merkle根的方法,并由
func DefaultProofRuntime() (prt *merkle.ProofRuntime)ingithub.com/bnb-chain/bsc/core/vm/lightclient/multistoreproof.go指定
(6) 如上图所示,它将首先跳转到 func (op IAVLValueOp) Run
func (op IAVLValueOp) Run(args [][]byte) ([][]byte, error) { if len(args) != 1 { return nil, cmn.NewError("Value size is not 1") } value := args[0]
// Compute the root hash and assume it is valid. // The caller checks the ultimate root later. root := op.Proof.ComputeRootHash() err := op.Proof.Verify(root) if err != nil { return nil, cmn.ErrorWrap(err, "computing root hash") } // XXX What is the encoding for keys? // We should decode the key depending on whether it's a string or hex, // maybe based on quotes and 0x prefix? err = op.Proof.VerifyItem([]byte(op.key), value) if err != nil { return nil, cmn.ErrorWrap(err, "verifying value") } return [][]byte{root}, nil}为通过上述步骤(1)中 MerkleProof.validateMerkleProof的验证 ,上述代码需要满足两点要求
- 首先, 步骤(5)中函数
func (op IAVLValueOp) Run返回的return [][]byte{root}, nil结果需与步骤(4)函数func (poz ProofOperators) Verify中的args[0]参数匹配,即!bytes.Equal(root, args[0])。 - 其次,代码
err := op.Proof.Verify(root)与err = op.Proof.VerifyItem([]byte(op.key), value)的返回错误必须为nil
(7) 为了满足上述要求,关键在于函数 op.Proof.ComputeRootHash() in func (op IAVLValueOp) Run 计算所得的root是不可伪造的。因为,我们进一步深入函数 op.Proof.ComputeRootHash() 进行细节追踪:
- 首先跳转至
func (proof *RangeProof) ComputeRootHash() - 再跳转至
func (proof *RangeProof) _computeRootHash() - 随后调用函数
_computeRootHash()中的闭包func(path PathToLeaf, rightmost bool) - 最后调用到闭包中的
hash = (pathWithLeaf{Path: path, Leaf: nleaf,}).computeRootHash()
上述调用过程细节如下,有兴趣的读者可以进一步阅读代码
func (proof *RangeProof) ComputeRootHash() []byte { if proof == nil { return nil } rootHash, _ := proof.computeRootHash() return rootHash}
func (proof *RangeProof) _computeRootHash() (rootHash []byte, treeEnd bool, err error) { if len(proof.Leaves) == 0 { return nil, false, cmn.ErrorWrap(ErrInvalidProof, "no leaves") } if len(proof.InnerNodes)+1 != len(proof.Leaves) { return nil, false, cmn.ErrorWrap(ErrInvalidProof, "InnerNodes vs Leaves length mismatch, leaves should be 1 more.") }
// Start from the left path and prove each leaf.
// shared across recursive calls var leaves = proof.Leaves var innersq = proof.InnerNodes var COMPUTEHASH func(path PathToLeaf, rightmost bool) (hash []byte, treeEnd bool, done bool, err error)
// rightmost: is the root a rightmost child of the tree? // treeEnd: true iff the last leaf is the last item of the tree. // Returns the (possibly intermediate, possibly root) hash. COMPUTEHASH = func(path PathToLeaf, rightmost bool) (hash []byte, treeEnd bool, done bool, err error) {
// Pop next leaf. nleaf, rleaves := leaves[0], leaves[1:] leaves = rleaves
// Compute hash. hash = (pathWithLeaf{ Path: path, Leaf: nleaf, }).computeRootHash()
// -- snip --
// We're not done yet (leaves left over). No error, not done either. // Technically if rightmost, we know there's an error "left over leaves // -- malformed proof", but we return that at the top level, below. return hash, false, false, nil }
// Verify! path := proof.LeftPath rootHash, treeEnd, done, err := COMPUTEHASH(path, true) if err != nil { return nil, treeEnd, cmn.ErrorWrap(err, "root COMPUTEHASH call") } else if !done { return nil, treeEnd, cmn.ErrorWrap(ErrInvalidProof, "left over leaves -- malformed proof") }
// Ok! return rootHash, treeEnd, nil}
(8) 因此,从函数func (pwl pathWithLeaf) computeRootHash()中我们可以发现,步骤(6)中所述 root 仅与IAVL树的最左侧叶子节点及其路径级联的哈希相关。
// `computeRootHash` computes the root hash with leaf node.// Does not verify the root hash.func (pwl pathWithLeaf) computeRootHash() []byte { leafHash := pwl.Leaf.Hash() return pwl.Path.computeRootHash(leafHash)}为便于理解,我们给出了一个IAVL树的示意图。代码层面的理解可以参考samczsun's code。
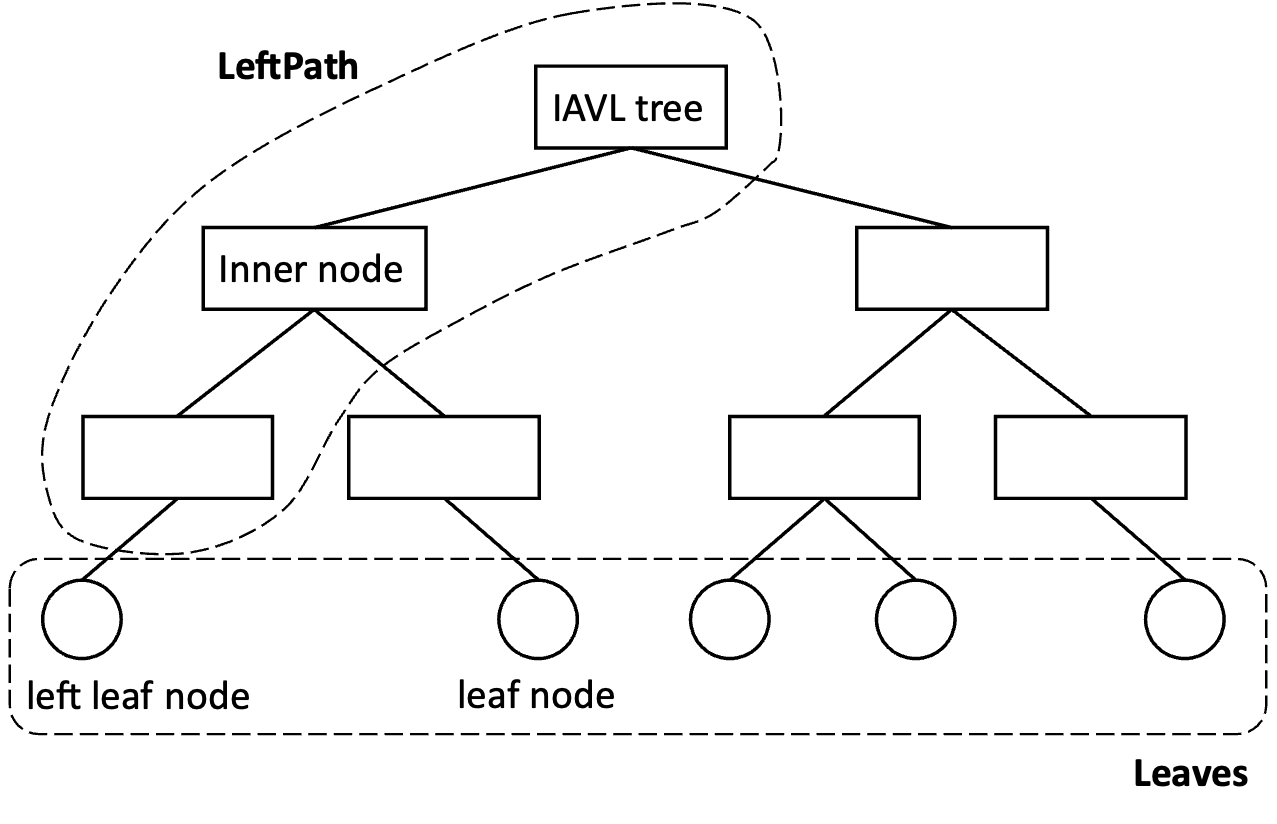
值得一提,上图中IAVL树中的数据类型在实际的结构体RangeProof 定义中的对应关系如下
xxxxxxxxxxtype RangeProof struct {// You don't need the right path because// it can be derived from what we have.LeftPath PathToLeaf `json:"left_path"`InnerNodes []PathToLeaf `json:"inner_nodes"`Leaves []proofLeafNode `json:"leaves"`// memoizerootVerified boolrootHash []byte // valid iff rootVerified is truetreeEnd bool // valid iff rootVerified is true}
因此,我们可以初步判断,在IAVL树的最左侧叶子节点及其路径的哈希级联过程中存在漏洞
核心的漏洞
(9) 最后,我们在代码库github.com/tendermint/iavl@v0.12.0/proof_path.go相关文件中,发现了中间节点哈希级联运算函数的漏洞。值得一提,尽管在BSC中调用的版本是v0.12.0,我们发现在该库的最新版本实现中仍然存在相应问题。无需担心的是,相关问题已经有热心开发者通过issue#579反馈给tendermint的相关开发团队。
xxxxxxxxxxfunc (pin proofInnerNode) Hash(childHash []byte) []byte { hasher := tmhash.New() buf := new(bytes.Buffer)
// -- snip -- // Where the bug is located if len(pin.Left) == 0 { if err == nil { err = amino.EncodeByteSlice(buf, childHash) } if err == nil { err = amino.EncodeByteSlice(buf, pin.Right) } } else { if err == nil { err = amino.EncodeByteSlice(buf, pin.Left) } if err == nil { err = amino.EncodeByteSlice(buf, childHash) } } // -- snip -- hasher.Write(buf.Bytes()) return hasher.Sum(nil)}
结合我们的图例,在上述函数 func (pin proofInnerNode) Hash(childHash []byte) 中,目标中间节点的左孩子 len(pin.Left) 长度不为0,根据代码逻辑,理应进入到else分支。在else分支中,我们发现其计算仅涵盖了pin.Left与childHash,而 pin.Right 并未纳入哈希计算中。因此,尽管一个恶意的节点被插入到IAVL树的证明中,其IAVL树的根哈希校验依旧可以通过,最终导致了此次攻击的发生。
其他潜在攻击
这次针对跨链桥的攻击比较特殊:往常桥出现问题往往是智能合约编写或者升级出现漏洞,而这次是因为区块链底层以来的库出现问题。
本次有问题的库为 github.com/cosmos/iavl,使用该库的项目包括 cosmos生态的核心组件 cosmos-sdk , IBC 等. 因此理论上使用cosmos-sdk构建的的项目、与cosmos跨链的项目都有可能受到影响,下文我们将分析是否有实际的攻击可能性。
针对COSMOS的潜在攻击
IBC protocol
IBC协议:IBC协议为COSMOS生态之间跨链的标准。IBC协议在跨链时,会使用 vector commitment 来验证源链的交易确实发生。IBC协议中通过 ics23 规定了可使用的向量证明,其中就包括了 iavl树的证明。因此我们需要调查 github.com/cosmos/iavl 的错误实现是否引入 ics23 的实现中。
ics23实现为ics-23-go 和 [confio/ics23](https://github.com/confio/ics23/blob/a4daeb4c24ce1be827829c0841446abc690c4f11/go/proof.go#L122。这里的实现没有使用iavl库,因此没有收到影响。
Cosmos-SDK
Cosmos-SDK 使用 IAVL+ 树来存储状态 , cosmos-sdk轻客户端使用 IAVL+ 树来证明某个状态的存在或者不存在。 Cosmos-SDK 提供了一个 工具将 IAVL树的证明 转换 为 ics23 Proof . 然而,没有证据表明SDK直接使用IAVL树的证明。 所以cosmos-sdk并没有受到影响
与COSMOS生态桥接的项目
Gravity bridge
Gravity bridge使用多签来做Evm与COSMOS之间的跨链,因此不受本次攻击影响。
EVMOS
EVMOS使用EVM上的 simple merkle 做跨链,不受影响。
结论
目前我们没有发现可能的攻击路径 . 然而直接使用 github.com/cosmos/iavl 库做验证的项目依旧可能存在被攻击的风险(即使已经升级SDK)。小心!
我们是谁
BHBA_DAO是一个由Beihang学生组成的去中心化学生自治组织。我们的愿景是为区块链爱好者提供一个学习交流的平台。我们将通过区块链科普活动、区块链行业研究、区块链技术开发活动等丰富多彩的活动帮助在校学生了解区块链生态,掌握区块链技术。欢迎所有在校学生加入我们,欢迎关注我们的推特@BHBA_DAO了解最新进展。